Leduc Holdem
Mar 02, 2020 Leduc Hold’em is a toy poker game sometimes used in academic research (first introduced in Bayes’ Bluff: Opponent Modeling in Poker). It is played with a deck of six cards, comprising two suits of three ranks each (often the king, queen, and jack — in our implementation, the ace, king, and queen).
- See full list on towardsdatascience.com.
- RLCard is an open-source toolkit for reinforcement learning research in card games. It supports various card environments with easy-to-use interfaces, including Blackjack, Leduc Hold'em, Texas Hold'em, UNO, Dou Dizhu and Mahjong.
- Demonstrate the effectiveness of this technique in Leduc Hold’em against opponents that use the UCT Monte Carlo tree search algorithm. Introduction Extensive-form games are a commonly-used, natural repre-sentation for sequential decision-making tasks. Their ability to model multiple agents, chance events, and imperfect in.
- Leduc Hold’em is a simplified version of Texas Hold’em. Rules can be found here.
RLCard is a toolkit for Reinforcement Learning (RL) in card games. It supports multiple card environments with easy-to-use interfaces. The goal of RLCard is to bridge reinforcement learning and imperfect information games. RLCard is developed by DATA Lab at Texas A&M University and community contributors.
- Official Website: http://www.rlcard.org
- Tutorial in Jupyter Notebook: https://github.com/datamllab/rlcard-tutorial
- Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.04376
- GUI: RLCard-Showdown
- Resources: Awesome-Game-AI
News:
- We have released RLCard-Showdown, GUI demo for RLCard. Please check out here!
- Jupyter Notebook tutorial available! We add some examples in R to call Python interfaces of RLCard with reticulate. See here
- Thanks for the contribution of @Clarit7 for supporting different number of players in Blackjack. We call for contributions for gradually making the games more configurable. See here for more details.
- Thanks for the contribution of @Clarit7 for the Blackjack and Limit Hold'em human interface.
- Now RLCard supports environment local seeding and multiprocessing. Thanks for the testing scripts provided by @weepingwillowben.
- Human interface of NoLimit Holdem available. The action space of NoLimit Holdem has been abstracted. Thanks for the contribution of @AdrianP-.
- New game Gin Rummy and human GUI available. Thanks for the contribution of @billh0420.
- PyTorch implementation available. Thanks for the contribution of @mjudell.
Cite this work
If you find this repo useful, you may cite:
Installation
Make sure that you have Python 3.5+ and pip installed. We recommend installing the latest version of rlcard with pip:
Alternatively, you can install the latest stable version with:
The default installation will only include the card environments. To use Tensorflow implementation of the example algorithms, install the supported verison of Tensorflow with:
To try PyTorch implementations, please run:
If you meet any problems when installing PyTorch with the command above, you may follow the instructions on PyTorch official website to manually install PyTorch.

We also provide conda installation method:
Conda installation only provides the card environments, you need to manually install Tensorflow or Pytorch on your demands.
Examples
Please refer to examples/. A short example is as below.
We also recommend the following toy examples in Python.
R examples can be found here.
Demo
Run examples/leduc_holdem_human.py to play with the pre-trained Leduc Hold'em model. Leduc Hold'em is a simplified version of Texas Hold'em. Rules can be found here.
We also provide a GUI for easy debugging. Please check here. Some demos:
Available Environments
We provide a complexity estimation for the games on several aspects. InfoSet Number: the number of information sets; InfoSet Size: the average number of states in a single information set; Action Size: the size of the action space. Name: the name that should be passed to rlcard.make to create the game environment. We also provide the link to the documentation and the random example.
| Game | InfoSet Number | InfoSet Size | Action Size | Name | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blackjack (wiki, baike) | 10^3 | 10^1 | 10^0 | blackjack | doc, example |
| Leduc Hold’em (paper) | 10^2 | 10^2 | 10^0 | leduc-holdem | doc, example |
| Limit Texas Hold'em (wiki, baike) | 10^14 | 10^3 | 10^0 | limit-holdem | doc, example |
| Dou Dizhu (wiki, baike) | 10^53 ~ 10^83 | 10^23 | 10^4 | doudizhu | doc, example |
| Simple Dou Dizhu (wiki, baike) | - | - | - | simple-doudizhu | doc, example |
| Mahjong (wiki, baike) | 10^121 | 10^48 | 10^2 | mahjong | doc, example |
| No-limit Texas Hold'em (wiki, baike) | 10^162 | 10^3 | 10^4 | no-limit-holdem | doc, example |
| UNO (wiki, baike) | 10^163 | 10^10 | 10^1 | uno | doc, example |
| Gin Rummy (wiki, baike) | 10^52 | - | - | gin-rummy | doc, example |
API Cheat Sheet
How to create an environment
You can use the the following interface to make an environment. You may optionally specify some configurations with a dictionary.
- env = rlcard.make(env_id, config={}): Make an environment.
env_idis a string of a environment;configis a dictionary that specifies some environment configurations, which are as follows.seed: DefaultNone. Set a environment local random seed for reproducing the results.env_num: Default1. It specifies how many environments running in parallel. If the number is larger than 1, then the tasks will be assigned to multiple processes for acceleration.allow_step_back: DefualtFalse.Trueif allowingstep_backfunction to traverse backward in the tree.allow_raw_data: DefaultFalse.Trueif allowing raw data in thestate.single_agent_mode: DefaultFalse.Trueif using single agent mode, i.e., Gym style interface with other players as pretrained/rule models.active_player: Defualt0. Ifsingle_agent_modeisTrue,active_playerwill specify operating on which player in single agent mode.record_action: DefaultFalse. IfTrue, a field ofaction_recordwill be in thestateto record the historical actions. This may be used for human-agent play.- Game specific configurations: These fields start with
game_. Currently, we only supportgame_player_numin Blackjack.
Once the environemnt is made, we can access some information of the game.
- env.action_num: The number of actions.
- env.player_num: The number of players.
- env.state_space: Ther state space of the observations.
- env.timestep: The number of timesteps stepped by the environment.
What is state in RLCard
State is a Python dictionary. It will always have observation state['obs'] and legal actions state['legal_actions']. If allow_raw_data is True, state will also have raw observation state['raw_obs'] and raw legal actions state['raw_legal_actions'].
Basic interfaces
The following interfaces provide a basic usage. It is easy to use but it has assumtions on the agent. The agent must follow agent template.
- env.set_agents(agents):
agentsis a list ofAgentobject. The length of the list should be equal to the number of the players in the game. - env.run(is_training=False): Run a complete game and return trajectories and payoffs. The function can be used after the
set_agentsis called. Ifis_trainingisTrue, it will usestepfunction in the agent to play the game. Ifis_trainingisFalse,eval_stepwill be called instead.
Advanced interfaces
For advanced usage, the following interfaces allow flexible operations on the game tree. These interfaces do not make any assumtions on the agent.
- env.reset(): Initialize a game. Return the state and the first player ID.
- env.step(action, raw_action=False): Take one step in the environment.
actioncan be raw action or integer;raw_actionshould beTrueif the action is raw action (string). - env.step_back(): Available only when
allow_step_backisTrue. Take one step backward. This can be used for algorithms that operate on the game tree, such as CFR. - env.is_over(): Return
Trueif the current game is over. Otherewise, returnFalse. - env.get_player_id(): Return the Player ID of the current player.
- env.get_state(player_id): Return the state that corresponds to
player_id. - env.get_payoffs(): In the end of the game, return a list of payoffs for all the players.
- env.get_perfect_information(): (Currently only support some of the games) Obtain the perfect information at the current state.
Running with multiple processes
RLCard now supports acceleration with multiple processes. Simply change env_num when making the environment to indicate how many processes would be used. Currenly we only support run() function with multiple processes. An example is DQN on blackjack
Library Structure
The purposes of the main modules are listed as below:

- /examples: Examples of using RLCard.
- /docs: Documentation of RLCard.
- /tests: Testing scripts for RLCard.
- /rlcard/agents: Reinforcement learning algorithms and human agents.
- /rlcard/envs: Environment wrappers (state representation, action encoding etc.)
- /rlcard/games: Various game engines.
- /rlcard/models: Model zoo including pre-trained models and rule models.
Evaluation
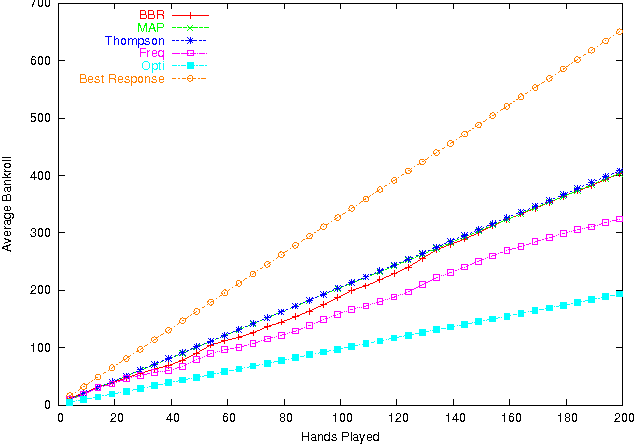
The perfomance is measured by winning rates through tournaments. Example outputs are as follows:
For your information, there is a nice online evaluation platform pokerwars that could be connected with RLCard with some modifications.
More Documents
For more documentation, please refer to the Documents for general introductions. API documents are available at our website.
Contributing
Contribution to this project is greatly appreciated! Please create an issue for feedbacks/bugs. If you want to contribute codes, please refer to Contributing Guide.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank JJ World Network Technology Co.,LTD for the generous support and all the contributions from the community contributors.
Blackjack¶

Blackjack is a globally popular banking game known as Twenty-One. Theobjective is to beat the dealer by reaching a higher score than thedealer without exceeding 21. In the toolkit, we implement a simpleversion of Blackjack. In each round, the player only has two options:“hit” which will take a card, and ‘stand’ which end the turn. The playerwill “bust” if his hands exceed 21 points. After the player completeshis hands (chooses “stand” and has not busted), the dealer then realshis hidden card and “hit” until obtaining at least 17 points.
State Representation of Blackjack¶
In this toy environment, we encode the stateas an array [player_score,dealer_score] where player_score isthe score currently obtained by the player, and the dealer_score isderived from the card that faces up from the dealer.
Action Encoding of Blackjack¶
There are two actions in the simple Blackjack. They areencoded as follows:
Action ID | Action |
|---|---|
0 | hit |
1 | stand |
Payoff of Blackjack¶
The player may receive a reward -1 (lose), 0 (tie), or 1 (win) in theend of the game.
Leduc Hold’em¶
Leduc Hold’em is a smaller version of Limit Texas Hold’em (firstintroduced in Bayes’ Bluff: Opponent Modeling inPoker). The deckconsists only two pairs of King, Queen and Jack, six cards in total.Each game is fixed with two players, two rounds, two-bet maximum andraise amounts of 2 and 4 in the first and second round. In the firstround, each player puts 1 unit in the pot and is dealt one card, thenstarts betting. In the second round, one public card is revealed first,then the players bet again. Finally, the player whose hand has the samerank as the public card is the winner. If neither, then the one withhigher rank wins. Other rules such as ‘fold’ can refer to Limit Texashold’em.
State Representation of Leduc Hold’em¶
The state is encoded as a vector of length 36. The first 3 elementscorrespond to hand card. The next 3 elements correspond to public card.The last 30 elements correspond the chips of the current player and theopponent (the chips could be in range 0~14) The correspondence betweenthe index and the card is as below.
Index | Meaning |
|---|---|
0~2 | J ~ K in hand |
3~5 | J ~ K as public card |
6~20 | 0 ~ 14 chips for the current player |
21~35 | 0 ~ 14 chips for the opponent |
Action Encoding of Leduc Hold’em¶
The action encoding is the same as Limit Hold’em game.
Payoff of Leduc Hold’em¶
The payoff is calculated similarly with Limit Hold’em game.
Limit Texas Hold’em¶
Texas Hold’em is a popular betting game. Each player is dealt twoface-down cards, called hole cards. Then 5 community cards are dealt inthree stages (the flop, the turn and the river). Each player seeks thefive best cards among the hole cards and community cards. There are 4betting rounds. During each round each player can choose “call”,“check”, “raise”, or “fold”.
In fixed limit Texas Hold’em. Each player can only choose a fixed amountof raise. And in each round the number of raises is limited to 4.
State Representation of Limit Texas Hold’em¶
The state is encoded as a vector of length 72. The first 52 elementsrepresent cards, where each element corresponds to one card. The hand isrepresented as the two hole cards plus the observed community cards sofar. The last 20 elements are the betting history. The correspondencebetween the index and the card is as below.
Index | Meaning |
|---|---|
0~12 | Spade A ~ Spade K |
13~25 | Heart A ~ Heart K |
26~38 | Diamond A ~ Diamond K |
39~51 | Club A ~ Club K |
52~56 | Raise number in round 1 |
37~61 | Raise number in round 2 |
62~66 | Raise number in round 3 |
67~71 | Raise number in round 4 |
Action Encoding of Limit Texas Hold’em¶
There 4 actions in Limit Texas Hold’em. They are encoded as below.
Action ID | Action |
|---|---|
0 | Call |
1 | Raise |
2 | Fold |
3 | Check |
Payoff of Limit Texas Hold’em¶
The stardard unit used in the leterature is milli big blinds per hand(mbb/h). In the toolkit, the reward is calculated based on big blindsper hand. For example, a reward of 0.5 (-0.5) means that the player wins(loses) 0.5 times of the amount of big blind.
Dou Dizhu¶
Doudizhu is one of the most popular Chinese card games with hundreds ofmillions of players. It is played by three people with one pack of 54cards including a red joker and a black joker. After bidding, one playerwould be the “landlord” who can get an extra three cards, and the othertwo would be “peasants” who work together to fight against the landlord.In each round of the game, the starting player must play a card or acombination, and the other two players can decide whether to follow or“pass.” A round is finished if two consecutive players choose “pass.”The player who played the cards with the highest rank will be the firstto play in the next round. The objective of the game is to be the firstplayer to get rid of all the cards in hand. For detailed rules, pleaserefer to Wikipedia orBaike.
In the toolkit, we implement a standard version of Doudizhu. In thebidding phase, we heuristically designate one of the players as the“landlord.” Specifically, we count the number of key cards orcombinations (high-rank cards and bombs), and the player with the mostpowerful hand is chosen as “lanlord.”
State Representation of Dou Dizhu¶
At each decision point of the game, the corresponding player will beable to observe the current state (or information set in imperfectinformation game). The state consists of all the information that theplayer can observe from his view. We encode the information into areadable Python dictionary. The following table shows the structure ofthe state:
Key | Description | Example value |
|---|---|---|
deck | A string of one pack of 54 cards with Black Joker and Red Joker. Each character means a card. For conciseness, we use ‘T’ for ‘10’. | 3333444455556666777788889999TTTTJJJJQQQQKKKKAAAA2222BR |
seen_cards | Three face-down cards distributed to the landlord after bidding. Then these cards will be made public to all players. | TQA |
landlord | An integer of landlord’s id | 0 |
self | An integer of current player’s id | 2 |
initial_hand | All cards current player initially owned when a game starts. It will not change with playing cards. | 3456677799TJQKAAB |
trace | A list of tuples which records every actions in one game. The first entry of the tuple is player’s id, the second is corresponding player’s action. | [(0, ‘8222’), (1, ‘pass’), (2, ‘pass’), (0 ‘6KKK’), (1, ‘pass’), (2, ‘pass’), (0, ‘8’), (1, ‘Q’)] |
played_cards | As the game progresses, the cards which have been played by the three players and sorted from low to high. | [‘6’, ‘8’, ‘8’, ‘Q’, ‘K’, ‘K’, ‘K’, ‘2’, ‘2’, ‘2’] |
others_hand | The union of the other two player’s current hand | 333444555678899TTTJJJQQAA2R |
current_hand | The current hand of current player | 3456677799TJQKAAB |
actions | The legal actions the current player could do | [‘pass’, ‘K’, ‘A’, ‘B’] |
State Encoding of Dou Dizhu¶
In Dou Dizhu environment, we encode the state into 6 feature planes. Thesize of each plane is 5*15. Each entry of a plane can be either 1 or 0.The 5 rows represent 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 corresonding cards, respectively. The15 columns start from “3” to “RJ” (Black Jack). For example, if we havea “3”, then the entry (1, 0) would be 1, and the rest of column 0 wouldbe 0. If we have a pair of “4”, then the entry (2, 1) would be 1, andthe rest of column 1 would be 0. Note that the current encoding methodis just an example to show how the feature can be encoded. Users areencouraged to encode the state for their own purposes by modifyingextract_state function in`rlcard/envs/doudizhu.py`__. The exampleencoded planes are as below:
Plane | Feature |
|---|---|
0 | the current hand |
1 | the union of the other two players’ hand |
2-4 | the recent three actions |
5 | the union of all played cards |
Action Abstraction of Dou Dizhu¶
The size of the action space of Dou Dizhu is 27472. This number is toolarge for learning algorithms. Thus, we make abstractions to theoriginal action space and obtain 309 actions. We note that some recentstudies also use similar abstraction techniques. The main idea of theabstraction is to make the kicker fuzzy and only focus on the major partof the combination. For example, “33344” is abstracted as “333 **”.When the predicted action of the agent is not legal, the agent willchoose “pass.”. Thus, the current environment is simple, since oncethe agent learns how to play legal actions, it can beat random agents.Users can also encode the actions for their own purposes (such asincreasing the difficulty of the environment) by modifyingdecode_action function inrlcard/envs/doudizhu.py. Users are alsoencouraged to include rule-based agents as opponents. The abstractionsin the environment are as below. The detailed mapping of action and itsID is inrlcard/games/doudizhu/jsondata/action_space.json:
Leduc Hold'em Tournaments
Type | Number ofActions | Number ofActions afterAbstraction | Action ID |
|---|---|---|---|
Solo | 15 | 15 | 0-14 |
pair | 13 | 13 | 15-27 |
Trio | 13 | 13 | 28-40 |
Trio withsingle | 182 | 13 | 41-53 |
Trio with pair | 156 | 13 | 54-66 |
Chain of solo | 36 | 36 | 67-102 |
Chain of pair | 52 | 52 | 103-154 |
Chain of trio | 45 | 45 | 155-199 |
Plane with solo | 21822 | 38 | 200-237 |
Plane with pair | 2939 | 30 | 238-267 |
Quad with solo | 1326 | 13 | 268-280 |
Quad with pair | 858 | 13 | 281-293 |
Bomb | 13 | 13 | 294-306 |
Rocket | 1 | 1 | 307 |
Pass | 1 | 1 | 308 |
Total | 27472 | 309 |
Payoff¶
If the landlord first get rid of all the cards in his hand, he will winand receive a reward 1. The two peasants will lose and receive a reward0. Similarly, if one of the peasant first get rid of all the cards inhand, both peasants will win and receive a reward 1. The landlord willlose and receive a reward 0.
Simple Dou Dizhu¶
Simple Dou Dizhu is a smaller version of Dou Dizhu. The deck onlyconsists of 6 ranks from ‘8’ to ‘A’ (8, 9, T, J, Q, K, A), there arefour cards with different suits in each rank. What’s more, unlikelandlord in Dou Dizhu, the landlord in Simple Dou Dizhu only has onemore card than the peasants. The rules of this game is the same as therules of Dou Dizhu. Just because each player gets fewer cards, they endthe game faster.
State Representation of Simple Dou Dizhu¶
This is almost the smae as the state representation of Dou Dizhu, butthe number of the ‘deck’ has reduced from 54 to 28, and the number ofthe ‘seen cards’ reduced from 3 to 1. The following table shows thestructure of the state:
Key | Description | Example value |
|---|---|---|
deck | A string of one pack of 28 cards without Black Joker and Red Joker. Each character means a card. For conciseness, we use ‘T’ for ‘10’. | 88889999TTTTJJJJQQQQKKKKAAAA |
seen_cards | One face-down card distributed to the landlord after bidding. Then the card will be made public to all players. | K |
landlord | An integer of landlord’s id | 0 |
self | An integer of current player’s id | 1 |
initial_hand | All cards current player initially owned when a game starts. It will not change with playing cards. | 8TTJJQQKA |
trace | A list of tuples which records every actions in one game. The first entry of the tuple is player’s id, the second is corresponding player’s action. | [(0, ‘8’), (1, ‘A’), (2, ‘pass’), (0, ‘pass’)] |
played_cards | As the game progresses, the cards which have been played by the three players and sorted from low to high. | [‘8’, ‘A’] |
others_hand | The union of the other two player’s current hand | 889999TTJJQQKKKAAA |
current_hand | The current hand of current player | 8TTJJQQK |
actions | The legal actions the current player could do | [‘J’, ‘TTJJQQ’, ‘TT’, ‘Q’, ‘T’, ‘K’, ‘QQ’, ‘8’, ‘JJ’] |
State Encoding of Simple Dou Dizhu¶
The state encoding is the same as Dou Dizhu game.
Action Encoding of Simple Dou Dizhu¶
The action encoding is the same as Dou Dizhu game. Because of thereduction of deck, the actions encoded have also reduced from 309 to131.
Payoff of Simple Dou Dizhu¶
The payoff is the same as Dou Dizhu game.
Mahjong¶
throughout the world since 20th century. It is commonly played by 4players. The game is played with a set of 136 tiles. In turn playersdraw and discard tiles until The goal of the game is to complete the leagal hand using the 14thdrawn tile to form 4 sets and a pair. We revised the game into a simpleversion that all of the winning set are equal, and player will win aslong as she complete forming 4 sets and a pair. Please refer the detailon Wikipedia orBaike.
State Representation of Mahjong¶
The state representation of Mahjong is encoded as 6 feature planes,where each plane has 34 X 4 dimensions. For each plane, the column ofthe plane indicates the number of the cards in the given cards set, andthe row of the plane represents each kind of cards (Please refer to theaction space table). The information that has been encoded can berefered as follows:
Plane | Feature |
|---|---|
0 | the cards in current player’s hand |
1 | the played cards on the table |
2-5 | the public piles of each players |
Action Space of Mahjong¶
There are 38 actions in Mahjong.
Action ID | Action |
|---|---|
0 ~ 8 | Bamboo-1 ~ Bamboo-9 |
9 ~ 17 | Characters-1 ~ Character-9 |
18 ~ 26 | Dots-1 ~ Dots-9 |
27 | Dragons-green |
28 | Dragons-red |
29 | Dragons-white |
30 | Winds-east |
31 | Winds-west |
32 | Winds-north |
33 | Winds-south |
34 | Pong |
35 | Chow |
36 | Gong |
37 | Stand |
Payoff of Mahjong¶
The reward is calculated by the terminal state of the game, wherewinning player is awarded as 1, losing players are punished as -1. Andif no one win the game, then all players’ reward will be 0.
No-limit Texas Hold’em¶
No-limit Texas Hold’em has similar rule with Limit Texas Hold’em. Butunlike in Limit Texas Hold’em game in which each player can only choosea fixed amount of raise and the number of raises is limited. In No-limitTexas Hold’em, The player may raise with at least the same amount asprevious raised amount in the same round (or the minimum raise amountset before the game if none has raised), and up to the player’sremaining stack. The number of raises is also unlimited.
State Representation of No-Limit Texas Hold’em¶
The state representation is similar to Limit Hold’em game. The state isrepresented as 52 cards and 2 elements of the chips of the players asbelow:
Index | Meaning |
|---|---|
0~12 | Spade A ~ Spade K |
13~25 | Heart A ~ Heart K |
26~38 | Diamond A ~ Diamond K |
39~51 | Club A ~ Club K |
52 | Chips of player 1 |
53 | Chips of player 2 |
Action Encoding of No-Limit Texas Hold’em¶
There are 6 actions in No-limit Texas Hold’em. They are encoded asbelow.
*Note: Starting from Action ID 3, the action means the amount playershould put in the pot when chooses ‘Raise’. The action ID from 3 to 5corresponds to the bet amount from half amount of the pot, full amountof the pot to all in.
Action ID | Action |
|---|---|
0 | Fold |
1 | Check |
2 | Call |
3 | Raise Half Pot |
4 | Raise Full Pot |
5 | All In |
Payoff of No-Limit Texas Hold’em¶
The reward is calculated based on big blinds per hand. For example, areward of 0.5 (-0.5) means that the player wins (loses) 0.5 times of theamount of big blind.
UNO¶
Uno is an American shedding-type card game that is played with aspecially deck.The game is for 2-10 players. Every player starts withseven cards, and they are dealt face down. The rest of the cards areplaced in a Draw Pile face down. Next to the pile a space should bedesignated for a Discard Pile. The top card should be placed in theDiscard Pile, and the game begins. The first player is normally theplayer to the left of the dealer and gameplay usually follows aclockwise direction. Every player views his/her cards and tries to matchthe card in the Discard pile. Players have to match either by thenumber, color, or the symbol/action. If the player has no matches, theymust draw a card. If that card can be played, play it. Otherwise, keepthe card. The objective of the game is to be the first player to get ridof all the cards in hand. For detailed rules, please refer toWikipedia or UnoRules. And in our toolkit, the number ofplayers is 2.
State Representation of Uno¶
In state representation, each card is represented as a string of colorand trait(number, symbol/action). ‘r’, ‘b’, ‘y’, ‘g’ represent red,blue, yellow and green respectively. And at each decision point of thegame, the corresponding player will be able to observe the current state(or information set in imperfect information game). The state consistsof all the information that the player can observe from his view. Weencode the information into a readable Python dictionary. The followingtable shows the structure of the state:
Key | Description | Example value |
|---|---|---|
hand | A list of the player’s currenthand. | [‘g-wild’, ‘b-0’, ‘g-draw_2’,‘y-skip’, ‘r-draw_2’, ‘y-3’,‘y-wild’] |
target | The top card in the Discardpile | ‘g-wild’ |
played_cards | As the game progresses, thecards which have been playedby the players | [‘g-3’, ‘g-wild’] |
others_hand | The union of the otherplayer’s current hand | [‘b-0’, ‘g-draw_2’, ‘y-skip’,‘r-draw_2’, ‘y-3’, ‘r-wild’] |
State Encoding of Uno¶
In Uno environment, we encode the state into 7 feature planes. The sizeof each plane is 4*15. Row number 4 means four colors. Column number 15means 10 number cards from 0 to 9 and 5 special cards—“Wild”, “Wild DrawFour”, “Skip”, “Draw Two”, and “Reverse”. Each entry of a plane can beeither 1 or 0. Note that the current encoding method is just an exampleto show how the feature can be encoded. Users are encouraged to encodethe state for their own purposes by modifying extract_state functionin `rlcard/envs/uno.py`__. The example encodedplanes are as below:
Plane | Feature |
|---|---|
0-2 | hand |
3 | target |
4-6 | others’ hand |
We use 3 planes to represnt players’ hand. Specifically, planes 0-2represent 0 card, 1 card, 2 cards, respectively. Planes 4-6 are thesame.
Action Encoding of Uno¶
There are 61 actions in Uno. They are encoded as below. The detailedmapping of action and its ID is inrlcard/games/uno/jsondata/action_space.json:
Action ID | Action |
|---|---|
0~9 | Red number cards from 0 to 9 |
10~12 | Red action cards: skip, reverse, draw 2 |
13 | Red wild card |
14 | Red wild and draw 4 card |
15~24 | green number cards from 0 to 9 |
25~27 | green action cards: skip, reverse, draw 2 |
28 | green wild card |
29 | green wild and draw 4 card |
30~39 | blue number cards from 0 to 9 |
40~42 | blue action cards: skip, reverse, draw 2 |
43 | blue wild card |
44 | blue wild and draw 4 card |
45~54 | yellow number cards from 0 to 9 |
55~57 | yellow action cards: skip, reverse, draw 2 |
58 | yellow wild card |
59 | yellow wild and draw 4 card |
60 | draw |
Payoff of Uno¶
Each player will receive a reward -1 (lose) or 1 (win) in the end of thegame.
Gin Rummy¶
Gin Rummy is a popular two person card game using a regular 52 card deck(ace being low). The dealer deals 11 cards to his opponent and 10 cardsto himself. Each player tries to form melds of 3+ cards of the same rankor 3+ cards of the same suit in sequence. If the deadwood count of thenon-melded cards is 10 or less, the player can knock. If all cards canbe melded, the player can gin. Please refer the detail onWikipedia.
Leduc Hold'em Strategy
If a player knocks or gins, the hand ends, each player put down theirmelds, and their scores are determined. If a player knocks, the opponentcan layoff some of his deadwood cards if they extend melds of theknocker. The score is the difference between the two deadwood counts ofthe players. If the score is positive, the player going out receives it.Otherwise, if the score is zero or negative, the opponent has undercutthe player going out and receives the value of the score plus a 25 pointundercut bonus.
Leduc Hold'em Poker
The non-dealer discards first (or knocks or gins if he can). If theplayer has not knocked or ginned, the next player can pick up thediscard or draw a card from the face down stockpile. He can knock or ginand the hand ends. Otherwise, he must discard and the next playercontinues in the same fashion. If the stockpile is reduced to two cardsonly, then the hand is declared dead and no points are scored.
State Representation of Gin Rummy¶
The state representation of Gin Rummy is encoded as 5 feature planes,where each plane is of dimension 52. For each plane, the column of theplane indicates the presence of the card (ordered from AS to KC). Theinformation that has been encoded can be referred as follows:
Plane | Feature |
|---|---|
0 | the cards in current player’s hand |
1 | the top card of the discard pile |
2 | the dead cards: cards in discard pile (excluding the top card) |
3 | opponent known cards: cards picked up from discard pile, but not discarded |
4 | the unknown cards: cards in stockpile or in opponent hand (but not known) |
Action Space of Gin Rummy¶
There are 110 actions in Gin Rummy.
Action ID | Action |
|---|---|
0 | score_player_0_action |
1 | score_player_1_action |
2 | draw_card_action |
3 | pick_up_discard_action |
4 | declare_dead_hand_action |
5 | gin_action |
6 - 57 | discard_action |
58 - 109 | knock_action |
Payoff of Gin Rummy¶
The reward is calculated by the terminal state of the game. Note thatthe reward is different from that of the standard game. A player whogins is awarded 1 point. A player who knocks is awarded 0.2 points. Thelosing player is punished by the negative of their deadwood countdivided by 100.
If the hand is declared dead, both players are punished by the negativeof their deadwood count divided by 100.
Settings¶
The following options can be set.
Option | Default value |
|---|---|
dealer_for_round | DealerForRound.Random |
stockpile_dead_card_count | 2 |
going_out_deadwood_count | 10 |
max_drawn_card_count | 52 |
is_allowed_knock | True |
is_allowed_gin | True |
is_allowed_pick_up_discard | True |
is_allowed_to_discard_picked_up_card | False |
is_always_knock | False |
is_south_never_knocks | False |
Variations¶
One can create variations that are easier to train by changing theoptions and specifying different scoring methods.